How Do Hybrid Cars Work?
Here is everything you need to know about hybrid cars – from how they work, what the differences are and how much they cost!
Hybrid cars use two or more energy sources, like a regular internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor, to power the vehicle. The great thing about having both an ICE and electric motor is they work together for the best fuel efficiency and performance.
At low speeds or idling, the electric motor takes over, reducing the load on the ICE and improving fuel efficiency. But, when the car needs more power for acceleration, the ICE steps in and provides additional power.
Hybrids also have a battery pack that stores energy from regenerative braking (more on this later). This energy can then be used by the electric motor for extra battery power, taking some of the load off the petrol engine. This combination of an ICE and electric motor provides a smooth, seamless drive experience with the best fuel efficiency.
There are three main types of hybrids: Self-charging, plug-in, and mild. We'll cover those later.
Find parking
Browse thousands of parking spaces for rent
Find parkingWhat's the Difference Between a Hybrid and a Conventional Car?
In a traditional car, energy is generated only by burning fuel in an ICE, which powers the wheels through a transmission. But in a hybrid, energy comes from both the ICE and electric motor, and the wheels can be powered by either one, or both together, depending on driving conditions.
Are Hybrid Cars More Fuel Efficient Than Petrol or Diesel Cars?
One big perk of hybrid cars is they're often more fuel efficient than petrol or diesel cars. By using the electric motor to help the ICE during acceleration and regenerative braking to recharge the battery, hybrid cars reduce fuel consumption and emissions. This means you'll save money at the pump and do your part for the environment.

What is a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)?
A type of hybrid you might have heard of is the Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV). They're similar to regular hybrids in that they have both an ICE and electric motor. But PHEVs also have a larger battery that can be charged by plugging the car into an electrical outlet. This allows PHEVs to run on electric power alone for short distances, before switching to hybrid mode.
What is a Self-Charging Hybrid?
A "self-charging hybrid" simply means the battery in the hybrid can be recharged through regenerative braking and energy from the ICE. No need to plug in the car, as it recharges automatically while driving.
What is a Mild Hybrid (MHEV)?
A mild hybrid is a type of hybrid that combines a conventional ICE with a small electric motor and battery. Unlike full hybrids, mild hybrids can't run on electric power alone. Instead, the electric motor helps the ICE, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
The electric motor is usually used during low-speed driving and acceleration, reducing the load on the ICE and improving fuel efficiency. The battery in a mild hybrid is usually smaller because it only helps the ICE, not powering the car on its own. Mild hybrids are a more affordable option for people who want to reduce fuel consumption and emissions without needing a full hybrid.
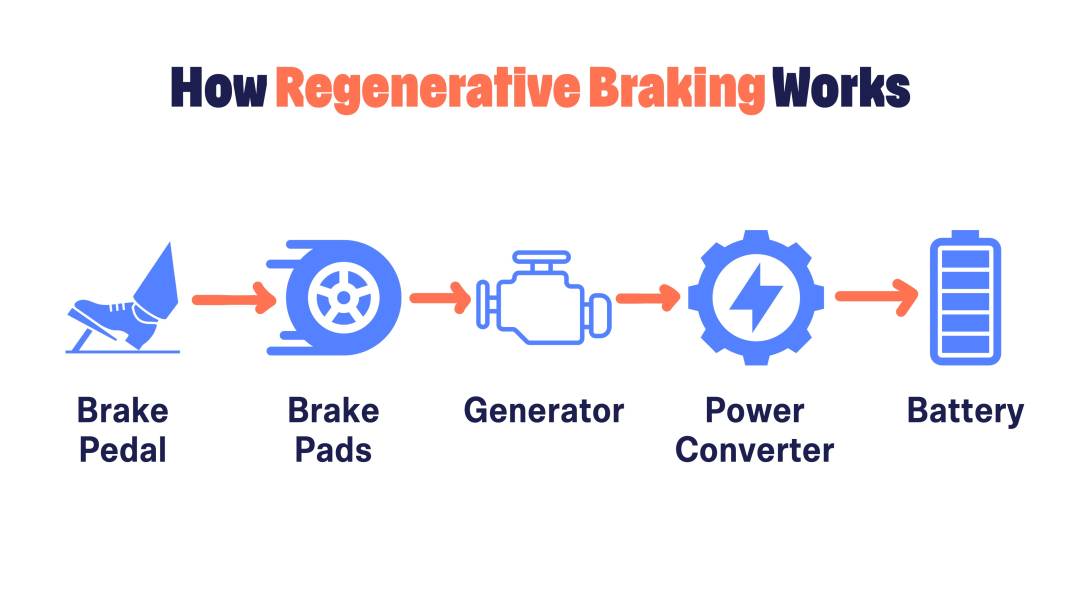
What is Regenerative Braking?
Regenerative braking is a technology used in hybrid and electric vehicles to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy and store it in the vehicle's battery. During regenerative braking, the electric motor in the vehicle acts as a generator, converting the energy generated by the vehicle's motion into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery.
When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor in the vehicle slows down the wheels and converts the energy generated by the vehicle's motion into electricity. This process reduces the amount of energy lost as heat through friction brakes and instead puts it back into the battery, where it can be used later to power the vehicle.
The result is improved fuel efficiency, longer battery life, and reduced wear and tear on the friction brakes. Additionally, regenerative braking can also help improve the driving experience, as it provides a more linear and smoother braking experience compared to traditional friction brakes.
What are the Benefits of Owning a Hybrid Car?
- Better fuel efficiency: Hybrid cars use a mix of an electric motor and a regular engine to run, which means they use less fuel compared to regular gas or diesel cars. This can lead to big fuel savings, especially for city drivers.
- Lower emissions: Hybrid cars emit less pollution compared to regular cars, making them a more eco-friendly option.
- Tax credits and incentives: Lots of hybrid cars can get tax credits and other incentives, which can help with the higher initial cost of the car.
- Improved performance: Hybrid cars can perform better than regular cars because the electric motor helps the engine.
- Smoother drive: The electric motor in a hybrid car provides a smooth and quiet ride, especially at low speeds.
No matter if you choose a regular hybrid, a PHEV, MHEV or a self-charging hybrid, you'll be making a smart choice for your wallet and the planet. Each type of hybrid has its own benefits, so do your research to find the one that's best for you.

What are the negatives of owning a hybrid car?
As with everything, there are some drawbacks to having a hybrid cars:- Higher upfront cost: Even with fuel savings and tax incentives, hybrid cars can still be more expensive to buy than regular cars.
- Limited driving range: Hybrid cars are more fuel-efficient, but the electric battery in a hybrid car is smaller than in a full electric car, meaning that hybrid cars have a limited range on electric power alone – check out our blog on how to improve the range of your electric vehicle for help with this!
- Complexity: Hybrid cars are more complex than regular cars, with two power sources and multiple systems that need to work together. This can lead to higher running costs and a trickier ownership experience – some garages/mechanics do not know the ins and outs of hybrid engines so well.
- Charging time: If you go for a PHEV, you'll need to recharge the battery, which can take several hours. This might not be ideal for drivers who need to travel long distances regularly.
- Reduced storage space: The battery and other components in a hybrid car can take up space in the boot, which can be an issue for drivers who need to carry a lot of stuff.
It's important to think about the pros and cons of owning a hybrid car before making a purchase. While hybrid cars are a great choice for many people, they may not be the right choice for everyone. By thinking about your driving habits, budget, and environmental concerns, you can figure out if a hybrid car is right for you.
Related
Does EV Range in Winter Drop?
How Much Does a Hybrid Car Cost?
The cost of a hybrid car is usually higher compared to a regular petrol/diesel car, but the gap is getting smaller. The extra cost of a hybrid car is because of the electric motor, battery pack, and other components needed for the hybrid system to work.
Remember that even though the upfront cost of a hybrid car may be higher, the long-term benefits, like better fuel efficiency and lower emissions, can offset the cost over time. Plus, many hybrid cars can get tax credits and rebates, which can further reduce the total cost.
So, the cost of a hybrid car is a factor to think about when choosing between a hybrid and a regular car, but it's just one of many factors.
Related
How Much Does It Cost To Install An Electric Car Charger?
Which are the best Hybrid Cars 2023?
Here are the top 10 hybrid cars to buy in 2023 from AutoExpress. A couple of special mentions go to the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, Ford Kuga PHEV, and if you're into that, the BMW 3 Series.
| Manufacturer | Model | Efficiency (mpg) |
Emissions (CO2) |
Price |
| Toyota | Yaris | 68.8 mpg | 92 g/km | £21,460 |
| Honda | Civic | 60.1 mpg | 108 g/km | £29,595 |
| Kia | Niro | 64.2 mpg | 100 g/km | £28,295 |
| Hyundai | Tucson | 49.6 mpg | 127 g/km | £33,370 |
| Kia | Sportage | 49.6 mpg | 129 g/km | £34,750 |
| Renault | Clio | 64.1 mpg | 99 g/km | £21,695 |
| Toyota | RAV4 | 50.4 mpg | 126 g/km | £36,060 |
| Lexus | NX | 47.8 mpg | 129 g/km | £42,760 |
| Toyota | Corolla | 62.7 mpg | 102 g/km | £29,610 |
| Kia | Sorento | 40.9 mpg | 158 g/km | £50,995 |
Hopefully, now you are an expert on Hybrid cars and can make an informed decision if its the right choice for you! If you are looking for short or long-term parking in the UK then we've probably got something for you.
Find parking
Browse thousands of parking spaces for rent
Find parkingElliot
Written 17th Apr 2023
